Table of Contents
Ingrown hairs can be a frustrating and painful problem, especially for those who regularly shave, wax, or tweeze. Removing an ingrown hair requires careful attention to avoid further irritation and potential infection. In this article, we will delve into the world of ingrown hairs, exploring their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you're looking to remove an ingrown hair or prevent future occurrences, our comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need. From understanding the signs of ingrown hair to learning safe methods for removing an ingrown hair, we'll cover it all. So, let's get started on this journey to smooth, healthy skin, and learn how to remove an ingrown hair with confidence.
Understanding Ingrown Hair: Symptoms and Causes of Ingrown Hair
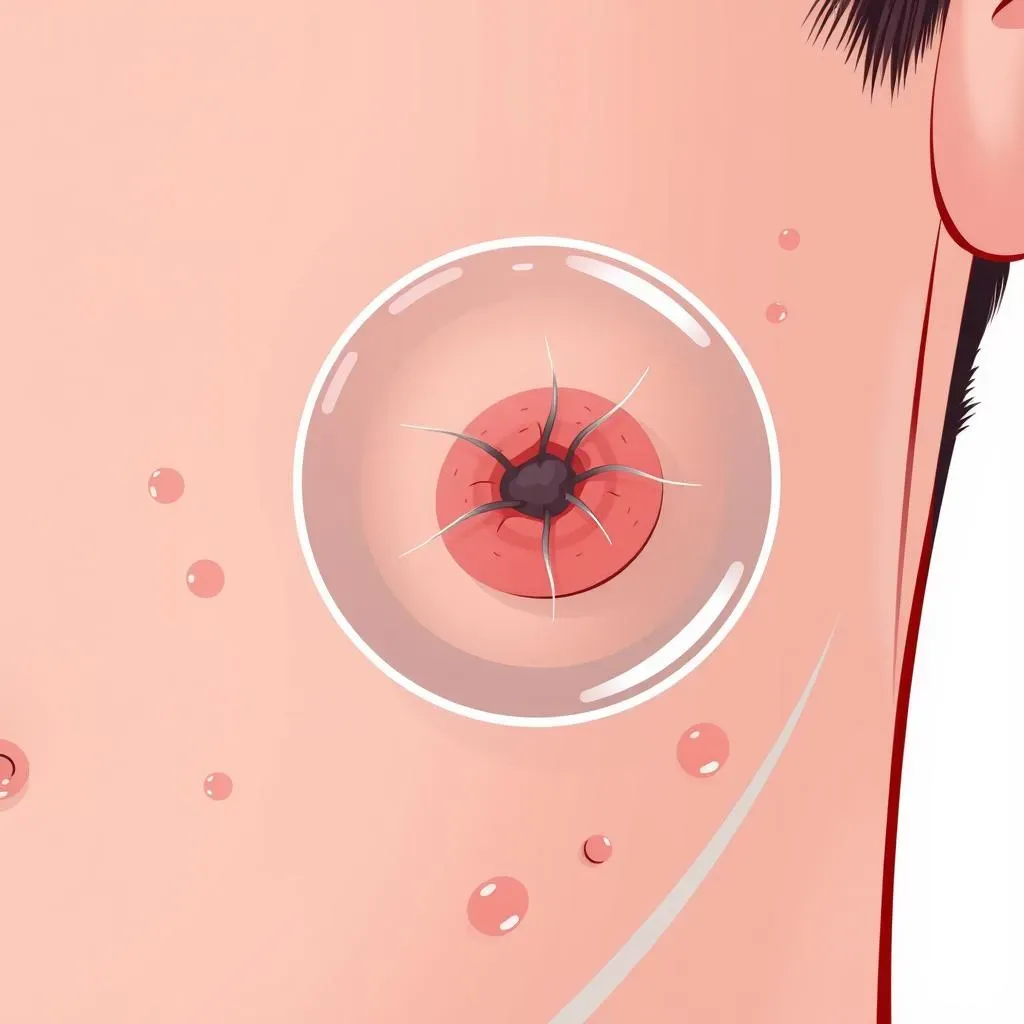
Understanding Ingrown Hair: Symptoms and Causes of Ingrown Hair
What is an Ingrown Hair?
An ingrown hair occurs when a strand of hair curls back into the skin instead of growing outward, leading to inflammation, redness, and sometimes infection. This condition is more common in individuals with curly, coarse, or thick hair, as well as those with skin of color. Ingrown hairs can appear anywhere on the body where hair is removed, such as the face, neck, armpits, bikini area, and legs.
Ingrown hairs often resemble small, raised bumps or spots on the skin, and may be accompanied by itching, pain, and swelling. In severe cases, they can become infected, leading to increased redness, pus, and scarring if left untreated.
Ingrown Hair Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
Raised bumps or spots | Small, inflamed areas where the hair has grown back into the skin |
Itching and redness | Irritation and inflammation around the affected area |
Pain and swelling | Tenderness and increased swelling, especially if infected |
Causes of Ingrown Hair
Ingrown hairs are often caused by hair removal methods such as shaving, waxing, and tweezing. When hair is cut close to the skin, it can cause the hair to grow back into the skin instead of outward. Curly or coarse hair is more prone to ingrown hairs due to its natural texture, which can make it more likely to curve back into the skin.
Other factors that contribute to ingrown hairs include:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of ingrown hairs are more likely to experience them
- Skin type: Those with thicker skin or skin of color are more susceptible
- Poor hair removal techniques: Shaving against the grain, using dull razors, or pulling the skin taut while shaving can increase the risk of ingrown hairs
Who is at Risk?
Anyone can develop ingrown hairs, but certain groups are more prone to them. These include:
Individuals with curly, coarse, or thick hair, as well as those with skin of color, are more likely to experience ingrown hairs. Additionally, people who shave, wax, or tweeze regularly are at a higher risk due to the frequent removal of hair.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of ingrown hairs is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. By recognizing the signs and taking steps to avoid hair removal methods that contribute to ingrown hairs, individuals can reduce their risk and maintain healthy, smooth skin.
Diagnosing Ingrown Hair: How to Identify and Treat Ingrown Hair
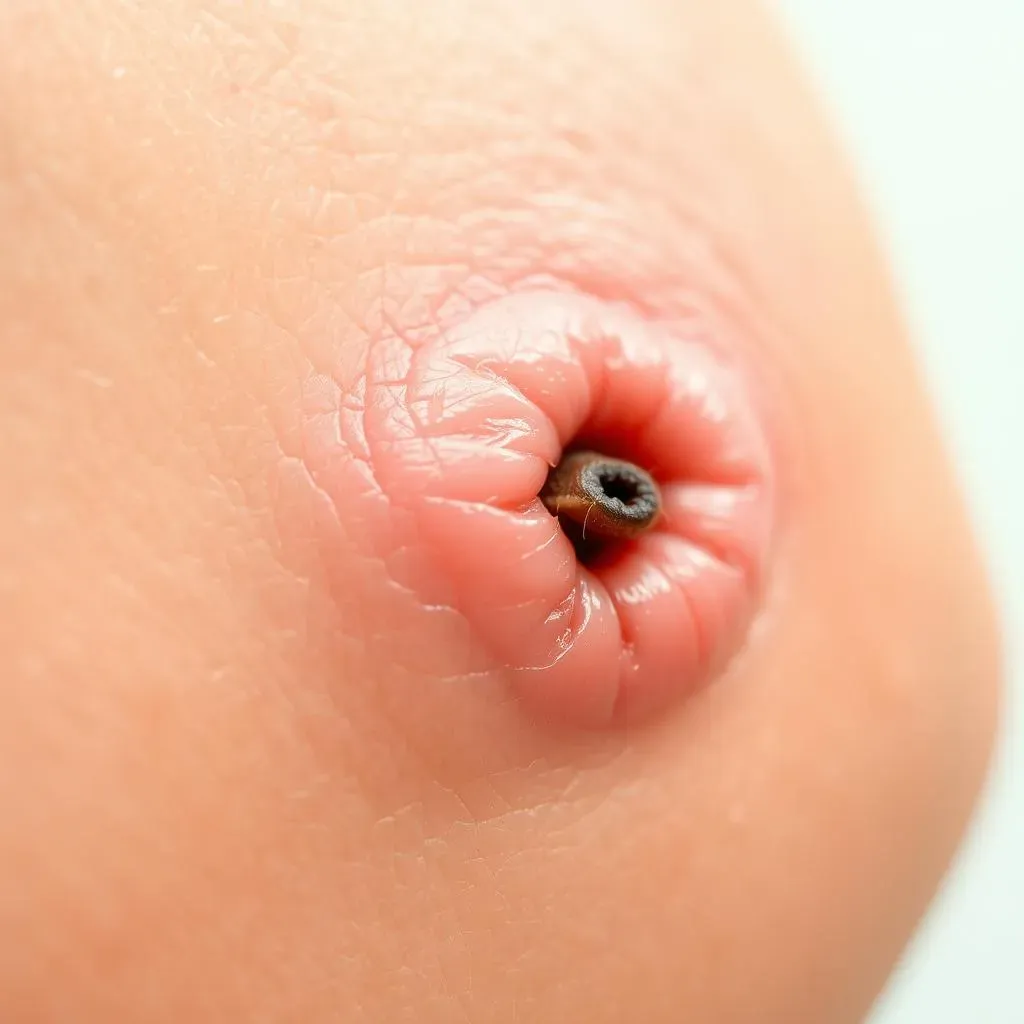
Diagnosing Ingrown Hair: How to Identify and Treat Ingrown Hair
Diagnosing ingrown hair typically involves a physical examination of the affected area. A healthcare provider will look for signs of inflammation, redness, and swelling, and may ask questions about your hair removal habits and skin care routine. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out other skin conditions.
Ingrown hairs can be treated with a variety of methods, depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may be treated with topical creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. More severe cases may require the use of antibiotics or corticosteroids to reduce swelling and promote healing.
Treatment Options | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
Topical creams | Hydrocortisone cream or antibiotic ointment | Mild cases |
Oral antibiotics | Prescribed for infected ingrown hairs | Infected cases |
Corticosteroid injections | Reduce swelling and inflammation | Severe cases |
In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the ingrown hair. This can be done using a sterile needle or tweezers, but it's essential to follow proper technique to avoid further irritation or infection. Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help bring the ingrown hair to the surface, making it easier to remove.
- Stop shaving or hair removal for a while
- Use depilatory products to dissolve the hair
- Apply warm compresses to bring the hair to the surface
- Use sterile needles or tweezers to carefully remove the hair
It's crucial to keep the affected area clean and avoid picking or scratching, as this can lead to infection and scarring. If ingrown hairs persist or become infected, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for further guidance and treatment.
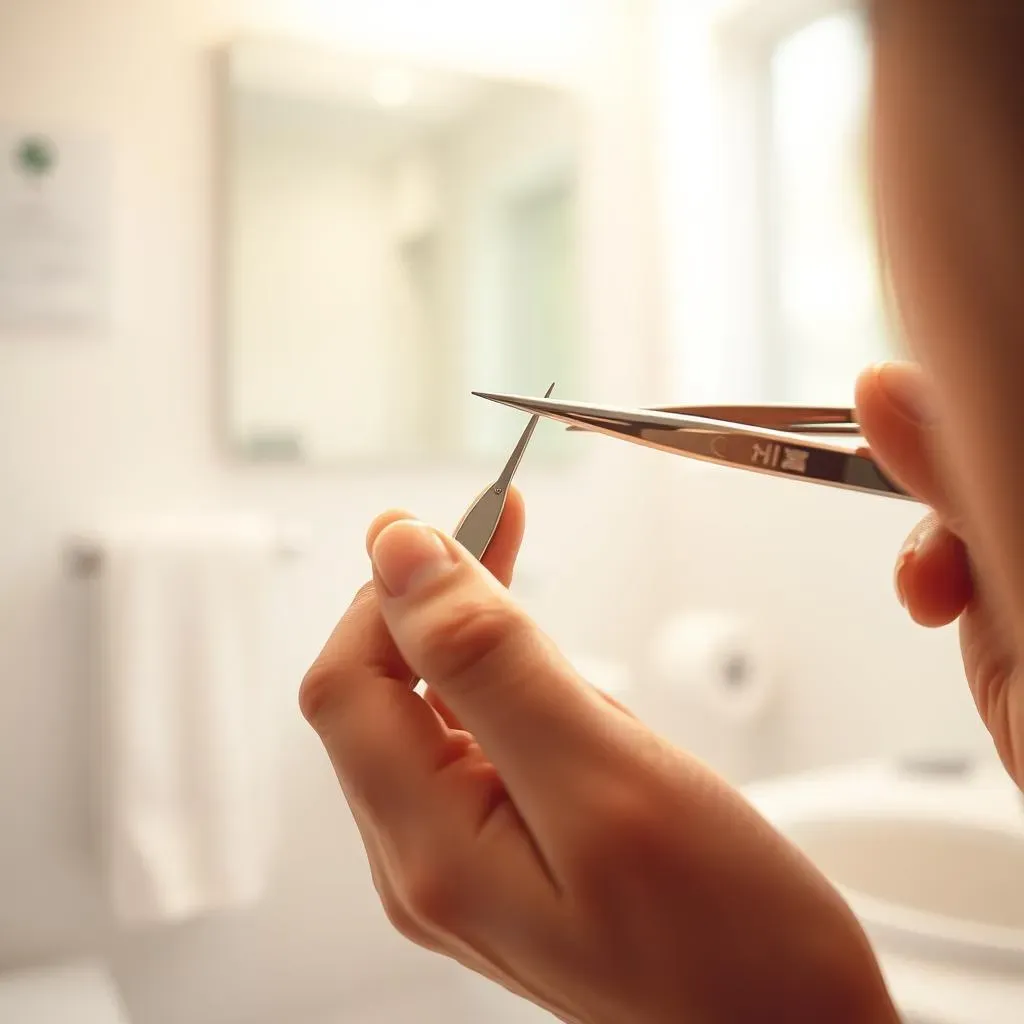
Removing an Ingrown Hair: Safe Methods for Ingrown Hair Removal

Removing an Ingrown Hair: Safe Methods for Ingrown Hair Removal
Preparing the Skin for Ingrown Hair Removal
Before attempting to remove an ingrown hair, it's essential to prepare the skin to minimize the risk of infection and promote healing. Exfoliating the skin gently can help bring the ingrown hair to the surface, making it easier to remove. Use a warm washcloth or an exfoliating scrub containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) to remove dead skin cells and other debris that may be trapping the hair.
Another method to bring the ingrown hair to the surface is by applying a warm compress to the affected area. Soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring it out thoroughly, and apply it to the skin for 5-10 minutes. Repeat this process several times a day to help loosen the hair and reduce swelling.
Exfoliation Methods | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
Physical exfoliation | Using a washcloth or exfoliating gloves | 1-2 times a week |
Chemical exfoliation | Using products containing AHAs or BHAs | 2-3 times a week |
Enzyme exfoliation | Using products containing enzymes like papain or bromelain | 1-2 times a week |
Safe Removal Techniques
Once the ingrown hair is accessible, it's crucial to remove it safely to avoid pushing it further into the skin or causing infection. Using a sterile needle or tweezers is the most common method for removing ingrown hairs. Start by cleaning the area with soap and water, then gently grasp the hair with the tweezers as close to the skin as possible. Pull the hair out in the direction of growth, taking care not to pull too hard and cause further irritation.
Alternatively, a sterile needle can be used to carefully tease out the ingrown hair. Insert the needle under the hair and gently lift it out, taking care not to puncture the skin. Apply an antibacterial ointment after removal to prevent infection.
- Use sterile equipment to prevent infection
- Remove the hair in the direction of growth
- Avoid digging or forcing the hair, as this can cause further irritation
- Apply an antibacterial ointment after removal
Post-Removal Care
After removing an ingrown hair, it's essential to keep the area clean and promote healing. Apply an antibacterial ointment to the affected area and cover it with a bandage to protect it from further irritation. Avoid scratching or picking at the area, as this can lead to infection and scarring.
Keep the area moisturized with a gentle, fragrance-free lotion to promote skin health and reduce the risk of future ingrown hairs. Avoid shaving or engaging in other hair removal activities for a while, allowing the skin time to heal and reducing the risk of further irritation.
Post-Removal Care Tips | Benefits |
|---|---|
Apply antibacterial ointment | Prevents infection and promotes healing |
Cover with a bandage | Protects the area from further irritation |
Moisturize the skin | Promotes skin health and reduces ingrown hair risk |
Preventing Ingrown Hair: Tips for Avoiding Ingrown Hair Growth

Preventing Ingrown Hair: Tips for Avoiding Ingrown Hair Growth
Proper Hair Removal Techniques
One of the most effective ways to prevent ingrown hairs is to use proper hair removal techniques. When shaving, it's essential to shave in the direction of hair growth, not against it. Shaving against the grain can cause the hair to become trapped under the skin, leading to ingrown hairs. Additionally, using a sharp razor and shaving cream can help reduce friction and prevent the hair from being pushed back into the skin.
Other hair removal methods, such as waxing and tweezing, can also contribute to ingrown hairs if not done correctly. It's crucial to follow proper technique and maintain clean equipment to minimize the risk of ingrown hairs. For waxing, make sure the skin is clean and dry, and remove the wax in the opposite direction of hair growth. When tweezing, pull the hair out in the direction of growth, taking care not to pull too hard and cause irritation.
Hair Removal Method | Tips for Prevention | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
Shaving | Shave in the direction of hair growth, use a sharp razor and shaving cream | Low-Moderate |
Waxing | Remove wax in the opposite direction of hair growth, keep skin clean and dry | Moderate-High |
Tweezing | Pull hair out in the direction of growth, avoid pulling too hard | High |
Exfoliation and Skincare
Regular exfoliation is essential for preventing ingrown hairs. Exfoliating helps remove dead skin cells and other debris that can trap hairs and cause them to grow back into the skin. Use a gentle exfoliating scrub or a chemical exfoliant containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) one to three times a week, depending on your skin type and needs.
A good skincare routine can also help prevent ingrown hairs. Keep your skin moisturized with a fragrance-free lotion, and avoid using harsh products that can strip the skin of its natural oils. Additionally, avoid tight clothing that can cause friction and irritation, especially in areas prone to ingrown hairs.
- Exfoliate 1-3 times a week
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products
- Moisturize regularly
- Avoid tight clothing
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can also help prevent ingrown hairs. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote skin health. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also essential for keeping the skin hydrated and supple. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can damage the skin and increase the risk of ingrown hairs.
Getting enough sleep and managing stress through techniques like meditation or exercise can also help reduce the risk of ingrown hairs. Stress can cause inflammation, which can contribute to ingrown hairs and other skin issues.
Lifestyle Change | Benefits |
|---|---|
Healthy diet | Promotes skin health and reduces inflammation |
Hydration | Keeps skin hydrated and supple |
Stress management | Reduces inflammation and promotes overall well-being |
Advanced Ingrown Hair Treatments: Professional Solutions for Severe Cases

Advanced Ingrown Hair Treatments: Professional Solutions for Severe Cases
Electrolysis and Laser Hair Removal
For individuals who experience frequent or severe ingrown hairs, electrolysis or laser hair removal may be a more permanent solution. These treatments target the hair follicle, reducing the growth of new hairs and minimizing the risk of ingrown hairs. Electrolysis involves inserting a fine needle into the hair follicle and applying a small electrical charge to destroy the root. Laser hair removal uses a laser to target the melanin in the hair follicle, heating it up and inhibiting future growth.
Both electrolysis and laser hair removal require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results. They can be more expensive than other hair removal methods, but they offer a long-term solution for individuals who struggle with ingrown hairs. It's essential to find a qualified practitioner to perform these treatments, as improper technique can lead to complications.
Treatment | Description | Number of Sessions |
|---|---|---|
Electrolysis | Destroys hair follicle with electrical charge | Multiple sessions |
Laser Hair Removal | Targets melanin in hair follicle with laser | 3-6 sessions |
Prescription Medications
In some cases, ingrown hairs may require prescription-strength medications to treat underlying conditions such as inflammation or infection. Topical corticosteroids can reduce swelling and redness, while oral antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infected ingrown hairs. In severe cases, retinoid medications can be used to promote cell turnover and prevent ingrown hairs from forming.
It's essential to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider when using prescription medications. They can help determine the best course of treatment and ensure that any underlying conditions are properly addressed. Additionally, medications should be used in conjunction with good skincare habits and proper hair removal techniques to achieve optimal results.
- Topical corticosteroids: reduce inflammation and swelling
- Oral antibiotics: treat infected ingrown hairs
- Retinoid medications: promote cell turnover and prevent ingrown hairs
Surgical Removal
In rare cases, surgical removal may be necessary for ingrown hairs that are severely infected or persistent. This involves making a small incision in the skin to remove the ingrown hair and any surrounding infected tissue. Surgical removal is typically performed under local anesthesia and may require stitches to close the incision.
After surgical removal, it's crucial to keep the area clean and follow post-operative instructions to promote healing and prevent infection. Surgical removal is usually a last resort, and other treatment options should be explored before considering this method.
Surgical Removal | Risks and Benefits | Post-Operative Care |
|---|---|---|
Removes infected tissue and ingrown hair | Risks include infection, scarring, and bleeding | Keep area clean, apply antibacterial ointment, and follow doctor's instructions |
Conclusion: Taking Control of Ingrown Hair
Ingrown hairs can be a nuisance, but with the right knowledge and techniques, you can effectively remove an ingrown hair and prevent future occurrences. By understanding the causes and symptoms of ingrown hairs, and using proper methods for removal and prevention, you can achieve healthier, smoother skin. Remember to always prioritize gentle exfoliation, proper shaving techniques, and good skincare routines to minimize the risk of ingrown hairs. If your ingrown hair persists or becomes infected, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for further guidance. With patience and the right approach, you can say goodbye to ingrown hairs and hello to radiant, healthy-looking skin.
